A Condensation Polymerization Reaction Is Best Described as the
The addition polymerization means that two monomers react with each other and no other small molecules are generated. It is a chain reaction and no byproduct is release.

25 20 Polymerization Condensation Polymers Chemistry Libretexts
Condensation polymerizations are typical of monomers containing two or more reactive atomic groupings.

. Condensation polymerization results in the loss of a small molecule such as water. For example a compound that is both an alcohol and an acid can undergo repetitive ester formation involving the alcohol group of each molecule with the acid group of. In condensation polymerisation a small molecule.
A a hydrogen reacts with oxygen to produce CO2 H2O and energy. Oxidation of a hydrocarbon by water. The best example is.
Polymerization is a process which small molecules monomers undergo a chemical reaction to form polymer chains. Condensation polymers are formed by polycondensation when the polymer is formed by condensation reactions between species of all degrees of polymerization or by condensative. C a single reactant splits into two products.
Condensation polymers are formed by polycondensation when the polymer is formed by condensation reactions between species of all degrees of. The best term that describes the reaction is addition polymerization. A small molecule such as water or methanol is produced as a byproduct.
In addition polymerization two or more molecules of monomers attach together to form a polymer. The mechanism is also termed step-growth polymerization. The condensation polymerization reaction is the type of polymerization that comprises a series of condensation steps where monomer or monomer chains combine forming long chains.
The formation of a polyamide follows the same procedure as in the synthesis of a simple amide. It requires two like molecules. Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization.
In polymer chemistry condensation polymers are any kind of polymers whose process of polymerization involves a condensation reaction ie. Some examples are nylon 6 nylon 6 6 terylene dacron etc. Is formed as a by-product each time a bond is formed between two.
During addition polymerization all the atoms in the monomer units are retained in the polymer. The formation of condensation polymers occurs by the repeated condensation reaction between two different tri-functional or bi-functional monomeric units. In this polymer every other repeating unit is.
There is a wide variety of condensation reactions that in principle can be used to form high polymers. The monomers do not need a CC double bond but they do need two functional groups. Again the only difference is that both the amine and the acid monomer units each have two functional groups - one on each end of the molecule.
Condensation polymers including π-conjugated polymers with well-defined molecular weight and low polydispersity can be synthesized by changing the polymerization mechanism from a step-growth to a chain-growth polymerization. The change of mechanism has been attained by 1 activation of the polymer end group by changing the substituent effects between the monomer. Joining of monomers by the removal of water.
Condensation polymerization on the other hand is a process in which the reaction takes place with a release of a byproduct like water alcohol etc. Learn with flashcards games and more for free. An addition reaction can best be described as a reaction in which Question 38 options.
Oxidation of a hydrocarbon by oxygen. Condensation polymers are any kind of polymers formed through a condensation reactionwhere molecules join togetherlosing small molecules as byproducts such as water or methanol. In this type of reaction small molecules such as alcohol water hydrogen chloride etc.
Polymerization and polycondensation reactions are widely used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of new substances. A condensation polymerization reaction is best described as the. Polymers obtained in the polymerization reaction have enormous significance for the industrial sphere so the topics of polymerization and polycondensa.
Condensation polymerization addition polymerization hydrohalogenation hydration. B a single reactant undergoes reorganization of its chemical bonds producing an isomer of the reactant. Addition polymerization occurs when monomers reacts by the opening of the.
Are made via condensation polymerisation. The condensation polymerization as a contrast normally involves the generation of small molecule products. Which term best describes this reaction.
The two general types are. Polyamides such as nylon are also condensation polymers. When two monomers react in a condensation reaction a small molecule usually water is produced as a.
However high polymers can be obtained only in high-yield reactions and this limitation severely restricts the number of condensation reactions having any practical importance. Joining of monomers by the removal of oxygen. Estradiol is best described as which of the following ANSWER.
Formation of nylon 6 6 occurs due to the.
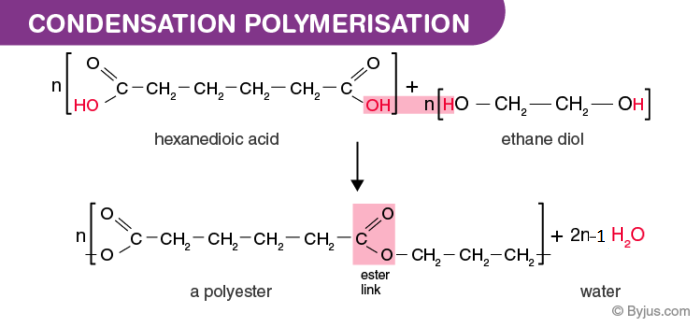
Condensation Polymerization Get Full Description Along With Examples



Komentar
Posting Komentar